Organizations are increasingly adopting automation to boost efficiency, reduce overhead, and improve accuracy—market value hit $635.24 million in 2022. But automation implantation isn’t an endeavor that should be executed impulsively or arbitrarily. Companies must approach automation initiatives with precision, thought, and targeted intent to achieve success. Rushed and careless implementation has produced a 78 percent failure rate.
So how can an organization ensure it properly establishes and scales automation for 100 percent success?
Through an automation factory.
What Is an Automation Factory?
An automation factory is an end-to-end strategy unique to an organization to help it automate multiple areas—often enterprise-wide—uniformly and efficiently. The model is a step-by-step process template that can be used to automate each/any area of the enterprise in a controlled manner. The factory can be custom designed for an organization’s unique requirements. It's referred to as a “factory” because the model process can be used again and again—much like an assembly line used to produce a product.
Benefits of an Automation Factory
An automation factory provides a holistic framework that guides decision-makers and stakeholders through all phases of an automation initiative and provides many benefits. Four of the most critical are:
- Alignment
The processes and stages involved in automation factory ensure that the organization is aligned with business outcomes throughout every step. - Consistency
An automation factory establishes consistency and a common approach across various teams and allows asset sharing, which supports scalability. - Clearly Defined Strategy
A well-planned roadmap ensures that the right problems are targeted and match with the most appropriate tools. - Organizational Interoperability
A dedicated automation model provides synergy between teams as it guards against ad-hoc solutions that cause fragmentation and cannot be scaled.
What Critical Elements Can an Automation Strategy Help Identify or Define?
- Strategy & Governance
An automation factory can help identify whose approval is required for buy-in, the key business drivers the proposed automation would improve, and the available budget for automaton investment. - Program Management
For program management, an automation factory can facilitate opportunity identification and prioritization, ROI estimation and tracking, metrics (KPI) definition, resource planning, and risk and dependency management. - Program Execution
Here, an automation factory will help determine what resources and infrastructure are needed for the execution of the automation strategy; software development and life cycle, and quality control; and offer post-production support (bug fixing, improvements for metrics calibrations). - Enterprise Enablement
For enterprise enablement, an automation factory can answer many questions such as: How do we integrate the new automation tools into our existing workflows? How do our workflows need to change to incorporate the new automation strategy? With whom do we need to collaborate? How do we inform everyone in the org who needs to change their practices to use the newlyp implemented automation strategy? How do we educate those users? - Technology Enablement
Technology enablement will benefit by discovering what solutions or capabilities does an organization need for our high-impact use cases and what is already available or needs to be built in-house.
6 Stages of an Automation Factory
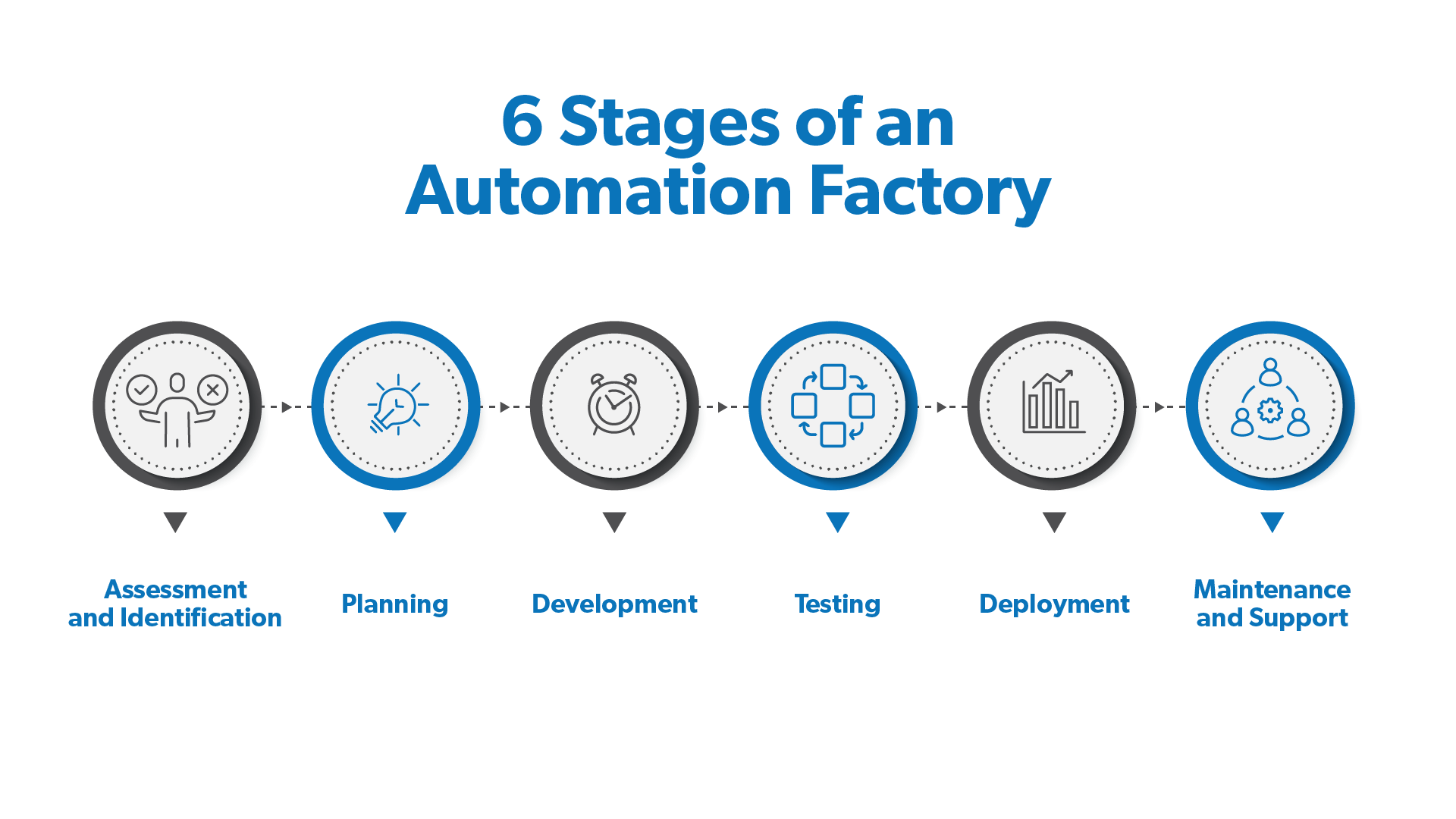
- Assessment and Identification
This is where critical process assessments take place, such as feasibility, business case, and best. It’s also the stage for idea identification, cost-benefit analysis, security approvals, and access approval. - Evaluation
Next, critical metrics are analyzed assessments are evaluated and analyses to create a detailed process design and walkthrough. Risk approvals are also secured. - Planning and Development
Here requirements are reviewed to ensure no critical functions were missed. Test strategies are also developed along with a project tracker, and the project tool may get approved. Code development and design can begin, and the solution can be reviewed for scalability. - Testing
In this stage the code should be complete, and the test plan can be reviewed and tested. Additionally, quality assurance, user acceptance testing and environment is setup, and the bot should have an ID to use within the system like a user. - Deployment
Now it’s time to check production readiness, secure all required approvals, fix bugs, monitor health of automation, and log all action and initial issues. - Maintenance and Support
Finally, the transition to operations team can take place and a review of automation performance for stability. Also, a metrics dashboard and monitoring can be set up.
Organizations that develop a comprehensive automation factory can save substantial time, money, and backtracking. A clearly mapped path with checks and balances helps ensure that the automation initiative is on track and is being applied correctly and appropriately. An automation factory also grants transparency to leaders and stakeholders and paints a clear picture of benefits, coming changes, and execution process.
For more information about establishing an automation factory for your organization, watch the Becker’s webinar: Strategic Automation Playbook



